304 Stainless Steel is the most versatile and commonly used stainless steel currently available for applications having corrosion resistance, high-temperature, and/or high-pressure requirements. The 304 grade is an austenitic stainless steel, meaning that it contains high levels of chromium and nickel and low levels of carbon. This combination gives 304 Stainless Steel strength, formability and resistance to corrosion.
There are several grades of 304 commonly used throughout the process piping industry. These include 304, 304H, 304L, and 304/304L. Typically containing at least 18% chromium and a minimum of 8% nickel, they are often referred to as 18-8 Stainless Steel.
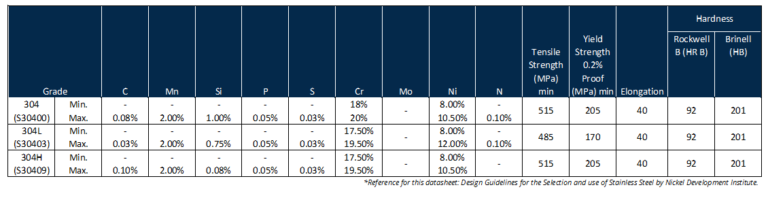
All Stainless Steel grades have an individual UNS (United Number System) Number:
• 304H (UNS S30409) has a max carbon content of 0.10% and is often
used in high temperature applications such as molten salt.
• 304L (UNS S30403) is a low-carbon variation with a max carbon
content of 0.03% and is often touted for its weldability.
• 304 straight-grade (UNS S30400) has a max carbon content of 0.08%
and is often used in food processing and heat exchangers.
• 304/304L Dual Certified meets the chemical and mechanical properties
of both 304 and 304L.
Tube, pipe, fittings, flanges, valves, and hardware are all manufactured with various types of 304 grade stainless steel in accordance with internationally recognized standards including ASTM International and ASME International. The following chart gives some more information about 304:
Stainless Steel Solves Problems
304 Stainless Steel Resists Oxidation
Oxidation can be a large problem. For example, other metals such as carbon steel will deteriorate over time in an outdoor or corrosive environment. Using 304 is usually an option, reducing maintenance and improving appearance. 304 has a wide range of operating temperatures making it quite versatile. Initial material and production costs can often be offset over time with reduced maintenance costs.
304 Stainless Steel Holds Up to Heat Cycling
Engineering and maintenance professionals often turn to 304 because it can withstand extreme heat cycling and remains strong for long-term service in hot applications such as ovens, boilers, and turbines. 304 guards against fatigue from continuous heat cycles and offers a long lifespan. In addition to the corrosion and temperature characteristics, 304 and 304L can be formed, machined, and have excellent welding characteristics. This combination of physical and technical attributes makes stainless steel a popular choice for handrails and guardrails and in the power generation, automotive, and process piping industries.
304 Stainless Steel Supports Sanitary Applications
304 is the preferred material for sanitary and food processing applications. It can be polished to a smooth, mirror-like finish eliminating the buildup of microorganisms, debris or contamination; it can tolerate the harsh chemicals and high temperatures from steam cleaning; and it withstands the corrosive action of various acids found in fruits, meats, milk, and vegetables.
304 Stainless Steel Withstands Extreme Temperatures for Cryogenics
304 is commonly used in cryogenic applications because it can handle and store liquid gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and helium. Stainless Steel often increases in tensile and yield strengths as the temperature decreases, making it a superior choice for extreme cold and cryogenic services.
304 Stainless Steel Process Piping Applications
• Food Processing
• Dairy Industry
• Fatty Acids
• Oil and Gas Refineries
• Pharmaceuticals
• Breweries
• Pulp and Paper
• Petrochemicals
• Sprinkler Systems
As you can see, 304 stainless steel can be used for a wide variety of difficult applications, solving problems within the process piping industry.







